Fortran - 重回帰式計算(説明変数2個)!
Updated:
Fortran 95 で、説明(独立)変数2個、目的(従属)変数1個の「重回帰式」を計算する方法についての記録です。
0. 前提条件
- LMDE 3 (Linux Mint Debian Edition 3; 64bit) での作業を想定。
- GCC 6.3.0 (GFortran 6.3.0) でのコンパイルを想定。
1. アルゴリズムについて
当ブログ過去記事を参照のこと。
2. ソースコードの作成
- 連立方程式の解法にはガウスの消去法を使用。
File: regression_multi.f95
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
!****************************************************
! 重回帰式計算(2元限定)
!
! date name version
! 2018.12.18 mk-mode.com 1.00 新規作成
!
! Copyright(C) 2018 mk-mode.com All Rights Reserved.
!****************************************************
!
module const
! SP: 単精度(4), DP: 倍精度(8)
integer, parameter :: SP = kind(1.0)
integer(SP), parameter :: DP = selected_real_kind(2 * precision(1.0_SP))
end module const
module comp
use const
implicit none
private
public :: calc_reg_multi
contains
! 重回帰式計算
!
! :param(in) real(8) x(:, 2): 説明変数配列
! :param(in) real(8) y(:): 目的変数配列
! :param(out) real(8) c: 定数
! :param(out) real(8) v(2): 係数
subroutine calc_reg_multi(x, y, c, v)
implicit none
real(DP), intent(in) :: x(:, :), y(:)
real(DP), intent(out) :: c, v(2)
integer(SP) :: size_x, size_y, i
real(DP) :: mtx(3, 3), mtx_2(2, 3)
size_x = size(x) / 2
size_y = size(y)
if (size_x == 0 .or. size_y == 0) then
print *, "[ERROR] array size == 0"
stop
end if
if (size_x /= size_y) then
print *, "[ERROR] size(X) != size(Y)"
stop
end if
mtx(1, 1) = sum_p(y, y)
mtx(2, 1) = sum_p(y, x(:, 1))
mtx(3, 1) = sum_p(y, x(:, 2))
do i = 1, 2
mtx(1, i + 1) = sum_p(x(:, i), y)
mtx(2, i + 1) = sum_p(x(:, i), x(:, 1))
mtx(3, i + 1) = sum_p(x(:, i), x(:, 2))
end do
mtx_2 = transpose(reshape((/ &
& mtx(2, 2), mtx(3, 2), mtx(1, 2), &
& mtx(2, 3), mtx(3, 3), mtx(1, 3) &
& /), (/3, 2/)))
call gauss_e(2, mtx_2)
v = (/mtx_2(1, 3), mtx_2(2, 3)/)
c = calc_const(reshape((/y(:), x(:, 1), x(:, 2)/), (/size_x, 3/)), v)
end subroutine calc_reg_multi
! Sum-of-producsts computation
!
! :param(in) real(8) x(:): 実数配列
! :param(in) real(8) y(:): 実数配列
! :retrun real(8) sum_p: sum of products
real(DP) function sum_p(x, y)
implicit none
real(DP), intent(in) :: x(:), y(:)
integer(SP) :: size_x, size_y, i
real(DP) :: avg_x, avg_y
size_x = size(x)
size_y = size(y)
avg_x = sum(x) / size_x
avg_y = sum(y) / size_y
sum_p = sum((/((x(i) - avg_x) * (y(i) - avg_y), i=1,size_x)/))
end function sum_p
! Gaussian elimination
!
! :param(in) integer(4) n: 元数
! :param(inout) real(8) a(n,n+1): 係数配列
subroutine gauss_e(n, a)
implicit none
integer(SP), intent(in) :: n
real(DP), intent(inout) :: a(n, n + 1)
integer(SP) :: i, j
real(DP) :: d
! 前進消去
do j = 1, n - 1
do i = j + 1, n
d = a(i, j) / a(j, j)
a(i, j+1:n+1) = a(i, j+1:n+1) - a(j, j+1:n+1) * d
end do
end do
! 後退代入
do i = n, 1, -1
d = a(i, n + 1)
do j = i + 1, n
d = d - a(i, j) * a(j, n + 1)
end do
a(i, n + 1) = d / a(i, i)
end do
end subroutine gauss_e
! Constant term computation
!
! :param(in) real(8) a(:, 3): 配列(目的変数, 説明変数1, 説明変数2)
! :param(in) real(8) v(2): 係数
! :return real(8) c: 定数項
function calc_const(a, v) result(c)
implicit none
real(DP), intent(in) :: a(:, :), v(:)
real(DP) :: c
integer(SP) :: size_a, i
real(DP) :: s(3)
size_a = size(a(:,1))
s = (/(sum(a(:, i)), i=1,3)/)
c = s(1) / size_a
do i = 2, size_a
c = c - s(i) * v(i - 1) / size_a
end do
end function calc_const
end module comp
program regression_multi
use const
use comp
implicit none
real(DP) :: x(10, 2), y(10), c, v(2)
integer(SP) :: i
x = reshape((/ &
& 17.5_DP, 17.0_DP, 18.5_DP, 16.0_DP, 19.0_DP, &
& 19.5_DP, 16.0_DP, 18.0_DP, 19.0_DP, 19.5_DP, &
& 30.0_DP, 25.0_DP, 20.0_DP, 30.0_DP, 45.0_DP, &
& 35.0_DP, 25.0_DP, 35.0_DP, 35.0_DP, 40.0_DP &
& /), (/10, 2/))
y = (/ &
& 45.0_DP, 38.0_DP, 41.0_DP, 34.0_DP, 59.0_DP, &
& 47.0_DP, 35.0_DP, 43.0_DP, 54.0_DP, 52.0_DP &
& /)
do i = 1, 2
print '(A, I0, A, 10F8.2, A)', "説明変数 X(", i, ") = (", x(:, i), ")"
end do
print '(A, 10F8.2, A)', "目的変数 Y = (", y, ")"
print '(A)', "---"
call calc_reg_multi(x, y, c, v)
print '(A, F14.8)', "定数項 = ", c
print '(A, F14.8)', "係数-1 = ", v(1)
print '(A, F14.8)', "係数-2 = ", v(2)
end program regression_multi
3. ソースコードのコンパイル
$ gfortran -o regression_multi regression_multi.f95
4. 動作確認
$ ./regression_multi
説明変数 X(1) = ( 17.50 17.00 18.50 16.00 19.00 19.50 16.00 18.00 19.00 19.50)
説明変数 X(2) = ( 30.00 25.00 20.00 30.00 45.00 35.00 25.00 35.00 35.00 40.00)
目的変数 Y = ( 45.00 38.00 41.00 34.00 59.00 47.00 35.00 43.00 54.00 52.00)
---
定数項 = -34.71293084
係数-1 = 3.46981263
係数-2 = 0.53300948
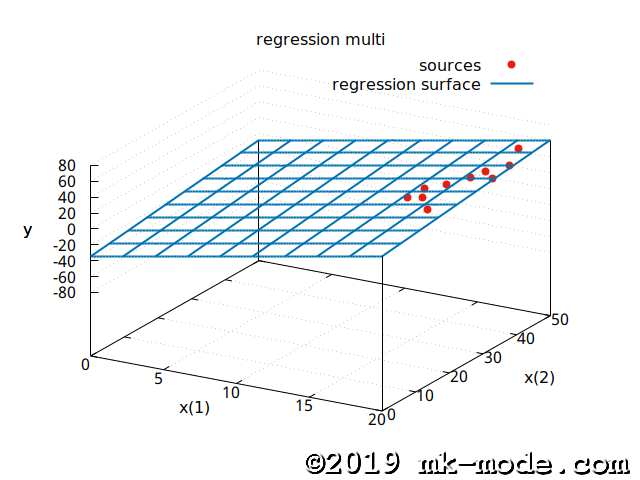
求まった回帰曲面は
\[y = -34.71293084 + 3.46981263 x_1 + 0.53300948 x_2\]ということである。
参考までに、回帰曲面と点を gnuplot で描画してみた。(説明変数 \(x_1, x_2\) を \(x, y\) 軸、目的変数 \(y\) を \(z\) 軸としてしている)(若干、分かりにくいかも)
以上。

Comments