Fortran - LU 分解(クラウト法(Crout method))!
Updated:
Fortran 95 で正方行列の LU 分解アルゴリズムを実装してみました。
今回使用する分解法は「クラウト法(Crout method)」
過去には Ruby で同じことをしました。
0. 前提条件
- LMDE 3 (Linux Mint Debian Edition 3; 64bit) での作業を想定。
- GCC 6.3.0 (GFortran 6.3.0) でのコンパイルを想定。
1. LU 分解について


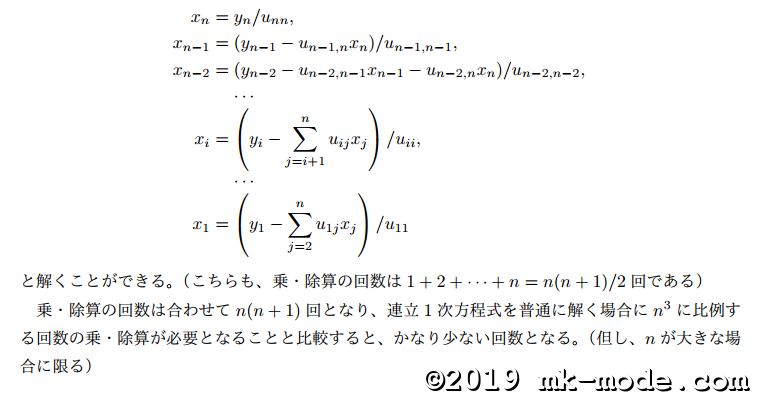
分解する方法には以下のようなものがある。(最初の3つがよく知られているもの)
- 外積形式ガウス法
- 内積形式ガウス法
- クラウト法
- ブロック形式ガウス法
- 縦ブロックガウス法
- 前進・後退代入
- …
2. LU 分解(クラウト法(Crout method))について
- LU 分解がなされたと仮定した上で、行列 U の対角要素を 1 として導出した方法。
- 長さ (1 ~ k - 1) のループ、長さ (k - n) のループの内、最も長いループを最内に移動可能なため、ベクトル計算機での実行性能が良い。
- 分解列および分解行の外側に 2 つの参照領域があり、どのようにデータ分割しても大量の通信が発生するため、分散メモリ型並列計算機での実装が困難。
- 参照領域があれば分解列と分解行は独立に計算が可能であるため、共有メモリ型並列計算機では並列化が可能。
3. Fortran ソースコードの作成
- 本来、 L と U の2つの行列に分けるものだが1つの行列にまとめている。(実際に LU 分解を使用する際に L と U を意識して取り扱えばよいだけなので)
File: lu_decomposition_3.f95
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
!************************************************************
! LU 分解(クラウト法(Crout method))
!
! date name version
! 2019.03.08 mk-mode.com 1.00 新規作成
!
! Copyright(C) 2019 mk-mode.com All Rights Reserved.
!************************************************************
!
module const
! SP: 単精度(4), DP: 倍精度(8)
integer, parameter :: SP = kind(1.0)
integer(SP), parameter :: DP = selected_real_kind(2 * precision(1.0_SP))
end module const
module lu
use const
implicit none
private
public :: decompose
contains
! LU 分解
! * クラウト法(Crout method)
!
! :param(inout) real(8) a(:,:): 行列
subroutine decompose(a)
implicit none
real(DP), intent(inout) :: a(:, :)
integer(SP) :: i, j, k, n
real(DP) :: s, tmp
n = int(sqrt(real(size(a))))
do k = 1, n
do i = k, n
s = sum((/(a(i, j) * a(j, k), j=1,k-1)/))
a(i, k) = a(i, k) - s
end do
if (a(1, 1) == 0.0_DP) then
print *, "Can't divide by 0 ..."
stop
end if
tmp = 1.0_DP / a(k, k)
do j = k + 1, n
s = sum((/(a(k, i) * a(i, j), i=1,k-1)/))
a(k, j) = (a(k, j) - s) * tmp
end do
end do
end subroutine decompose
end module lu
program lu_decomposition
use const
use lu
implicit none
character(9), parameter :: F_INP = "input.txt"
integer(SP), parameter :: UID = 10
integer(SP) :: n_row, n_col, i, j, k, n
real(DP) :: tmp
real(DP), allocatable :: a(:, :)
! ファイル OPEN
open (UID, file = F_INP, status = 'old')
! 行数・列数取得
read (UID, *) n_row, n_col
! 配列用メモリ確保
allocate(a(n_row, n_col))
! 行列取得
do i = 1, n_row
read (UID, *) a(i, :)
end do
call display(a)
! ファイル CLOSE
close (UID)
! LU 分解
call decompose(a)
print *, "-->"
call display(a)
! 配列用メモリ解放
deallocate(a)
stop
contains
subroutine display(a)
implicit none
real(DP), intent(in) :: a(:, :)
integer(SP) :: i, j, n
character(8) :: f
n = int(sqrt(real(size(a))))
f = "(IF8.2)"
write (f(2:2), '(I1)') n
do i = 1, n
write (*, f) a(i, :)
end do
endsubroutine display
end program lu_decomposition
4. ソースコードのコンパイル
$ gfortran -o lu_decomposition_3 lu_decomposition_3.f95
5. 動作確認
元の行列はテキストファイルから取り込むようにしているので、まず、テキストファイルを作成する。(1行目:行・列の数、2行目以降:1行ずつの値)
File: input.txt
1
2
3
4
3 3
2 -3 1
1 1 -1
3 5 -7
そして、実行。
$ ./lu_decomposition_3
2.00 -3.00 1.00
1.00 1.00 -1.00
3.00 5.00 -7.00
-->
2.00 -1.50 0.50
1.00 2.50 -0.60
3.00 9.50 -2.80
行列 U の対角成分を 1 として L と U に分けて LU を計算してみると、 A になるだろう。
以上。

Comments