C++ - LU 分解(外積形式ガウス法(outer-product form))!
Updated:
C++ で正方行列の LU 分解アルゴリズムを実装してみました。
今回使用する分解法は「外積形式ガウス法(outer-product form)」です。
過去には Ruby, Fortran で実装しています。
0. 前提条件
- Debian GNU/Linux 10.3 (64bit) での作業を想定。
- GCC 9.2.0 (G++ 9.2.0) (C++17) でのコンパイルを想定。
1. LU 分解について


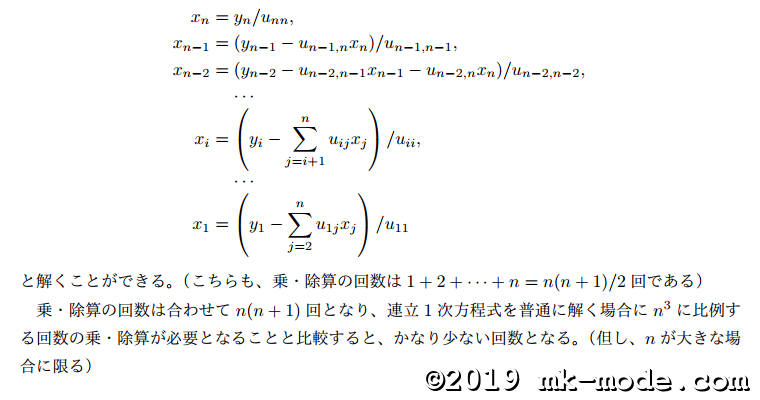
分解する方法には以下のようなものがある。(最初の3つがよく知られているもの)
- 外積形式ガウス法
- 内積形式ガウス法
- クラウト法
- ブロック形式ガウス法
- 縦ブロックガウス法
- 前進・後退代入
- …
2. LU 分解(外積形式ガウス法(outer-product form))について
- ガウス消去法と同等の操作で LU 分解する方法。
- 分解列の右側の領域が更新される方法で、 “right-looking” アルゴリズムと呼ばれる。
- 処理の中心の更新領域が多く、更新処理が分解行と分解列という少ないデータを所有するだけで要素ごとに独立して行えるため、並列化に向いている。
3. ソースコードの作成
- ファイル読み込み部分、計算部分、実行部分とソースファイルを分けている。
- 本来、 L と U の2つの行列に分けるものだが1つの行列にまとめている。(実際に LU 分解を使用する際に L と U を意識して取り扱えばよいだけなので)
- L の対角成分を 1 とみなすことを想定している。
よって、計算結果 LU の対角成分は U の対角成分である。
File: file.hpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
#ifndef LU_DECOMPOSITION_OUTER_PRODUCT_FILE_HPP_
#define LU_DECOMPOSITION_OUTER_PRODUCT_FILE_HPP_
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
class File {
std::string f_data;
public:
File(std::string f_data) : f_data(f_data) {}
bool get_text(std::vector<std::vector<double>>&);
};
#endif
File: file.cpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
#include "file.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
bool File::get_text(std::vector<std::vector<double>>& data) {
try {
// ファイル OPEN
std::ifstream ifs(f_data);
if (!ifs.is_open()) return false; // 読み込み失敗
// ファイル READ
std::string buf; // 1行分バッファ
while (getline(ifs, buf)) {
std::vector<double> rec; // 1行分ベクタ
std::istringstream iss(buf); // 文字列ストリーム
std::string field; // 1列分文字列
// 1行分文字列を1行分ベクタに追加
double s;
while (iss >> s)
rec.push_back(s);
// 1行分ベクタを data ベクタに追加
if (rec.size() != 0) data.push_back(rec);
}
} catch (...) {
std::cerr << "EXCEPTION!" << std::endl;
return false;
}
return true; // 読み込み成功
}
File: lu_decomposition.hpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
#ifndef LU_DECOMPOSITION_OUTER_PRODUCT_LU_DECOMPOSITION_HPP_
#define LU_DECOMPOSITION_OUTER_PRODUCT_LU_DECOMPOSITION_HPP_
#include <vector>
class LuDecomposition {
std::vector<std::vector<double>> data; // 元データ
public:
LuDecomposition(std::vector<std::vector<double>>& data) : data(data) {}
// コンストラクタ
unsigned int get_size(); // 行列サイズ取得
bool lu_decompose_outer_product(std::vector<std::vector<double>>&);
// LU 分解(外積形式ガウス法)
};
#endif
File: lu_decomposition.cpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
#include "lu_decomposition.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
/**
* @brief 行列サイズ取得
*
* @return 行列サイズ(unsigned int)
*/
unsigned int LuDecomposition::get_size() {
return data.size();
}
/**
* @brief LU 分解(外積形式ガウス法(outer-product form))
* (L の対角要素を 1 とする)
*
* @param[ref] m x m 行列(配列) mtx (double)
* @return 真偽(bool)
* @retval true 成功
* @retval false 失敗
*/
bool LuDecomposition::lu_decompose_outer_product(
std::vector<std::vector<double>>& mtx
) {
std::size_t i; // loop インデックス
std::size_t j; // loop インデックス
std::size_t k; // loop インデックス
std::size_t m; // 行列サイズ
double tmp; // 一時退避用
try {
m = get_size();
for (k = 0; k < m; k++) {
if (mtx[k][k] == 0) {
std::cout << "[ERROR] Can't divide by 0!" << std::endl;
return false; // 計算失敗
}
tmp = 1.0 / mtx[k][k];
for (i = k + 1; i < m; i++)
mtx[i][k] *= tmp;
for (j = k + 1; j < m; j++) {
tmp = mtx[k][j];
for (i = k + 1; i < m; i++)
mtx[i][j] -= mtx[i][k] * tmp;
}
}
} catch (...) {
return false; // 計算失敗
}
return true; // 計算成功
}
File: lu_decomposition_outer_product.cpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
/***********************************************************
LU 分解
: 外積形式ガウス法(outer-product form)
DATE AUTHOR VERSION
2020.07.24 mk-mode.com 1.00 新規作成
Copyright(C) 2020 mk-mode.com All Rights Reserved.
***********************************************************/
#include "lu_decomposition.hpp"
#include "file.hpp"
#include <cstdlib> // for EXIT_XXXX
#include <iomanip> // for setprecision
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
std::string f_data; // データファイル名
std::vector<std::vector<double>> data; // データ配列
std::size_t i; // loop インデックス
std::size_t j; // loop インデックス
unsigned int m; // 行列サイズ
try {
// コマンドライン引数のチェック
if (argc != 2) {
std::cerr << "[ERROR] Number of arguments is wrong!\n"
<< "[USAGE] ./lu_decomposition_outer_product <file_name>"
<< std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// ファイル名取得
f_data = argv[1];
// データ取得
File file(f_data);
if (!file.get_text(data)) {
std::cout << "[ERROR] Failed to read the file!" << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// 計算用オプジェクトのインスタンス化
LuDecomposition lu(data);
// 行列サイズ
m = lu.get_size();
// データ一覧出力
std::cout << "A = " << std::endl;
std::cout << std::fixed << std::setprecision(4);
for (i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < m; j++)
std::cout << std::setw(10) << std::right << data[i][j];
std::cout << std::endl;
}
// 計算
if (!lu.lu_decompose_outer_product(data)) {
std::cout << "[ERROR] Failed to decompose!" << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// 結果出力
std::cout << "LU = " << std::endl;
std::cout << std::fixed << std::setprecision(4);
for (i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < m; j++)
std::cout << std::setw(10) << std::right << data[i][j];
std::cout << std::endl;
}
} catch (...) {
std::cerr << "EXCEPTION!" << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
4. ソースコードのコンパイル
まず、以下のように Makefile を作成する。(行頭のインデントはタブ文字)
File: Makefile
gcc_options = -std=c++17 -Wall -O2 --pedantic-errors
lu_decomposition_outer_product: lu_decomposition_outer_product.o file.o lu_decomposition.o
g++ $(gcc_options) -o $@ $^
lu_decomposition_outer_product.o : lu_decomposition_outer_product.cpp
g++ $(gcc_options) -c $<
file.o : file.cpp
g++ $(gcc_options) -c $<
lu_decomposition.o : lu_decomposition.cpp
g++ $(gcc_options) -c $<
run : lu_decomposition_outer_product
./lu_decomposition_outer_product
clean :
rm -f ./lu_decomposition_outer_product
rm -f ./*.o
.PHONY : run clean
そして、ビルド(コンパイル&リンク)。
$ make
5. 動作確認
まず、以下のような入力ファイル(元の行列)を用意する。
File: data.txt
1
2
3
2.00 -3.00 1.00
1.00 1.00 -1.00
3.00 5.00 -7.00
そして、実行。
$ ./lu_decomposition_outer_product data.txt
A =
2.0000 -3.0000 1.0000
1.0000 1.0000 -1.0000
3.0000 5.0000 -7.0000
LU =
2.0000 -3.0000 1.0000
0.5000 2.5000 -1.5000
1.5000 3.8000 -2.8000
行列 L の対角成分を 1 として L と U に分けて LU を計算してみると、 A になるだろう。
以上。

Comments