C++ - 単回帰曲線(自然対数回帰モデル)の計算!
Updated:
C++ で、数値からなる同サイズの配列2つを説明変数・目的変数とみなして単回帰曲線(自然対数回帰モデル)を計算する方法についての記録です。
今回は連立1次方程式を解くのに「ガウスの消去法」を使用します。
過去には Fortran 等で実装しています。
0. 前提条件
- Debian GNU/Linux 10.3 (64bit) での作業を想定。
- GCC 9.2.0 (G++ 9.2.0) (C++17) でのコンパイルを想定。
1. アルゴリズムについて
求める曲線を \(y = a + b \log_e{x}\) とすると、残差の二乗和 \(S\) は
\[\begin{eqnarray*} S = \sum_{i=1}^{N}(y_i - a - b\log_e{x})^2 \end{eqnarray*}\]となる。 \(a,b\) それぞれで偏微分したものを \(0\) とする。
\[\begin{eqnarray*} \frac{\partial S}{\partial a} &=& 2\sum_{i=1}^{N}(a+b\log_e{x_i} - y_i)= 0 \\ \frac{\partial S}{\partial b} &=& 2\sum_{i=1}^{N}(a+b\log_e{x_i} - y_i)\log_e{x_i}= 0 \end{eqnarray*}\]これらを変形すると、
\[\begin{eqnarray*} aN + b\sum_{i=1}^{N}\log_e{x_i} &=& \sum_{i=1}^{N}y_i \\ a\sum_{i=1}^{N}\log_e{x_i} + b\sum_{i=1}^{N}(\log_e{x_i})^2 &=& \sum_{i=1}^{N}(\log_e{x_{i}})y_i \end{eqnarray*}\]となる。これらの連立方程式を解けばよい。
2. ガウスの消去法による連立1次方程式の解法について
当ブログ過去記事を参照。
- C++ - 連立方程式解法(ガウスの消去法)!
- Ruby - 連立方程式解法(ガウスの消去法)!
- Python - 連立方程式解法(ガウスの消去法)!
- Fortran - 連立方程式解法(ガウスの消去法)!
3. ソースコードの作成
- ファイル読み込み部分、計算部分、実行部分とソースファイルを分けている。
File: file.hpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
#ifndef REGRESSION_CURVE_LN_FILE_HPP_
#define REGRESSION_CURVE_LN_FILE_HPP_
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
class File {
std::string f_data;
public:
File(std::string f_data) : f_data(f_data) {}
bool get_text(std::vector<std::vector<double>>&);
};
#endif
File: file.cpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
#include "file.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
bool File::get_text(std::vector<std::vector<double>>& data) {
try {
// ファイル OPEN
std::ifstream ifs(f_data);
if (!ifs.is_open()) return false; // 読み込み失敗
// ファイル READ
std::string buf; // 1行分バッファ
while (getline(ifs, buf)) {
std::vector<double> rec; // 1行分ベクタ
std::istringstream iss(buf); // 文字列ストリーム
std::string field; // 1列分文字列
// 1行分文字列を1行分ベクタに追加
double x, y;
while (iss >> x >> y) {
rec.push_back(x);
rec.push_back(y);
}
// 1行分ベクタを data ベクタに追加
if (rec.size() != 0) data.push_back(rec);
}
} catch (...) {
std::cerr << "EXCEPTION!" << std::endl;
return false;
}
return true; // 読み込み成功
}
File: calc.hpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
#ifndef REGRESSION_CURVE_LN_CALC_HPP_
#define REGRESSION_CURVE_LN_CALC_HPP_
#include <vector>
class Calc {
std::vector<std::vector<double>> data; // 元データ
std::vector<std::vector<double>> mtx; // 計算用行列
bool solve_ge(std::vector<std::vector<double>>&); // ガウスの消去法
public:
Calc(std::vector<std::vector<double>>& data) : data(data) {}
unsigned int cnt; // データ件数
bool reg_curve_ln(double&, double&); // 単回帰曲線(自然対数回帰)の計算
};
#endif
File: calc.cpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
#include "calc.hpp"
#include <cmath>
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
/**
* @brief 単回帰曲線(自然対数回帰)の計算
*
* @param[ref] a (double)
* @param[ref] b (double)
* @return 真偽(bool)
* @retval true 成功
* @retval false 失敗
*/
bool Calc::reg_curve_ln(double& a, double& b) {
unsigned int i; // loop インデックス
double s_lx = 0.0; // sum(log(x))
double s_lx2 = 0.0; // sum(log(x) * log(x))
double s_y = 0.0; // sum(y)
double s_lxy = 0.0; // sum(log(x) * y)
double x = 0.0; // x 計算用
double y = 0.0; // y 計算用
double lx = 0.0; // log(x) 計算用
try {
// データ数
cnt = data.size();
// sum(log(x)), sum(log(x) * log(x)), sum(y), sum(log(x) * y)
for (i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {
x = data[i][0];
y = data[i][1];
lx = std::log(x);
s_lx += lx;
s_lx2 += lx * lx;
s_y += y;
s_lxy += lx * y;
}
// 行列1行目
mtx.push_back({(double)cnt, s_lx, s_y});
// 行列2行目
mtx.push_back({s_lx, s_lx2, s_lxy});
// 計算(ガウスの消去法)
if (!solve_ge(mtx)) {
std::cout << "[ERROR] Failed to solve by the Gauss-Ellimination method!"
<< std::endl;
return false;
}
// a, b
a = mtx[0][2];
b = mtx[1][2];
} catch (...) {
return false; // 計算失敗
}
return true; // 計算成功
}
/**
* @brief ガウスの消去法
*
* @param[ref] 行列(配列) mtx (double)
* @return 真偽(bool)
* @retval true 成功
* @retval false 失敗
*/
bool Calc::solve_ge(std::vector<std::vector<double>>& mtx) {
int i; // loop インデックス
int j; // loop インデックス
int k; // loop インデックス
int n; // 元(行)の数
double d; // 計算用
try {
n = (int)mtx.size();
// 前進消去
for (k = 0; k < n - 1; k++) {
for (i = k + 1; i < n; i++) {
d = mtx[i][k] / mtx[k][k];
for (j = k + 1; j <= n; j++)
mtx[i][j] -= mtx[k][j] * d;
}
}
// 後退代入
for (i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
d = mtx[i][n];
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
d -= mtx[i][j] * mtx[j][n];
mtx[i][n] = d / mtx[i][i];
}
} catch (...) {
return false; // 計算失敗
}
return true; // 計算成功
}
File: regression_curve_ln.cpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
/***********************************************************
単回帰曲線(自然対数回帰モデル)計算
: y = a + b * ln(x)
: 連立方程式をガウスの消去法で解く方法
DATE AUTHOR VERSION
2020.05.28 mk-mode.com 1.00 新規作成
Copyright(C) 2020 mk-mode.com All Rights Reserved.
***********************************************************/
#include "calc.hpp"
#include "file.hpp"
#include <cstdlib> // for EXIT_XXXX
#include <iomanip> // for setprecision
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
std::string f_data; // データファイル名
std::vector<std::vector<double>> data; // データ配列
std::size_t i; // loop インデックス
double a; // 定数 a
double b; // 係数 b
try {
// コマンドライン引数のチェック
if (argc != 2) {
std::cerr << "[ERROR] Number of arguments is wrong!\n"
<< "[USAGE] ./regression_curve_ln <file_name>"
<< std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// ファイル名取得
f_data = argv[1];
// データ取得
File file(f_data);
if (!file.get_text(data)) {
std::cout << "[ERROR] Failed to read the file!" << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// データ一覧出力
std::cout << std::fixed << std::setprecision(4);
std::cout << "説明変数 X 目的変数 Y" << std::endl;
for (i = 0; i < data.size(); i++)
std::cout << std::setw(10) << std::right << data[i][0]
<< " "
<< std::setw(10) << std::right << data[i][1]
<< std::endl;
// 計算
Calc calc(data);
if (!calc.reg_curve_ln(a, b)) {
std::cout << "[ERROR] Failed to calculate!" << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// 結果出力
std::cout << std::fixed << std::setprecision(8);
std::cout << "---\n"
<< "a = " << std::setw(16) << std::right << a
<< "\n"
<< "b = " << std::setw(16) << std::right << b
<< std::endl;
} catch (...) {
std::cerr << "EXCEPTION!" << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
4. ソースコードのコンパイル
まず、以下のように Makefile を作成する。(行頭のインデントはタブ文字)
File: Makefile
gcc_options = -std=c++17 -Wall -O2 --pedantic-errors
regression_curve_ln: regression_curve_ln.o file.o calc.o
g++ $(gcc_options) -o $@ $^
regression_curve_ln.o : regression_curve_ln.cpp
g++ $(gcc_options) -c $<
file.o : file.cpp
g++ $(gcc_options) -c $<
calc.o : calc.cpp
g++ $(gcc_options) -c $<
run : regression_curve_ln
./regression_curve_ln
clean :
rm -f ./regression_curve_ln
rm -f ./*.o
.PHONY : run clean
そして、ビルド(コンパイル&リンク)。
$ make
5. 動作確認
まず、以下のような入力ファイルを用意する。
(各行は x と y の値)
File: data.txt
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
83 183
71 168
64 171
69 178
69 176
64 172
68 165
59 158
81 183
91 182
57 163
65 175
58 164
62 175
そして、ファイル名を引数に指定して実行。
$ ./regression_curve_ln data.txt
説明変数 X 目的変数 Y
83.0000 183.0000
71.0000 168.0000
64.0000 171.0000
69.0000 178.0000
69.0000 176.0000
64.0000 172.0000
68.0000 165.0000
59.0000 158.0000
81.0000 183.0000
91.0000 182.0000
57.0000 163.0000
65.0000 175.0000
58.0000 164.0000
62.0000 175.0000
---
a = -20.17729983
b = 45.62823794
参考までに、上記で使用した2変量の各点と作成された単回帰直線を gnuplot で描画してみた。
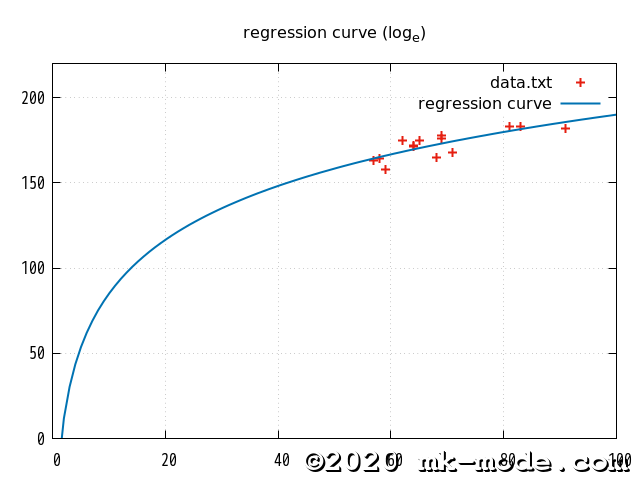
以上。

Comments