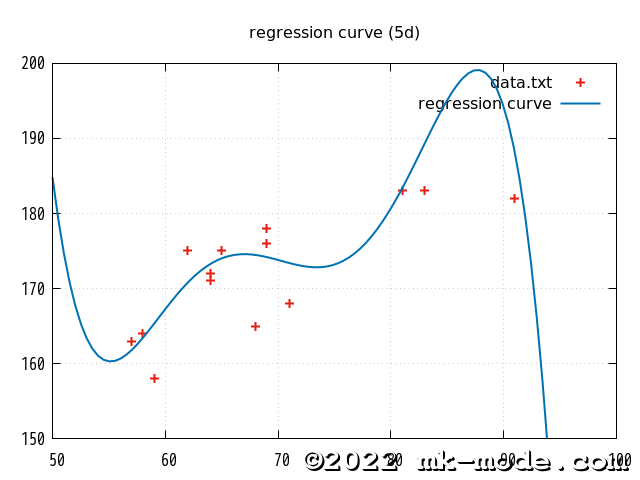
C++ - 単回帰曲線(5次回帰モデル)の計算!
Updated:
C++ で、数値からなる同サイズの配列2つを説明変数・目的変数とみなして単回帰曲線(5次回帰モデル)を計算する方法についての記録です。
今回は連立1次方程式を解くのに「ガウスの消去法(ピボット選択)」を使用します。
先日は Ruby で実装しています。。
0. 前提条件
- Debian GNU/Linux 11.3 (64bit) での作業を想定。
- GCC 11.2.0 (G++ 11.2.0) (C++17) でのコンパイルを想定。
- 連立方程式の解法(ガウスの消去法(ピボット選択))についての説明は割愛。(Web 上等で容易に確認可能)
1. 単回帰曲線(5次回帰モデル)の求め方
求める曲線を \(y=a+bx+cx^2+dx^3+ex^4+fx^5\) とすると、残差の二乗和 \(S\) は
\[S = \sum_{i=1}^{N}(y_i - a - bx_i - cx_i^2 - dx^3 - ex^4 - fx^5)^2\]となる。 \(a,b,c,d,e,f\) それぞれで偏微分したものを \(0\) とする。
\[\begin{eqnarray*} \frac{\partial S}{\partial a} &=& 2\sum_{i=1}^{N}(a+bx_i+cx_i^2+dx_i^3+ex_i^4 - y_i) = 0 \\ \frac{\partial S}{\partial b} &=& 2\sum_{i=1}^{N}(ax_i+bx_i^2+cx_i^3+dx_i^4+ex_i^5+fx_i^6 - x_{i}y_i) = 0 \\ \frac{\partial S}{\partial c} &=& 2\sum_{i=1}^{N}(ax_i^2+bx_i^3+cx_i^4+dx_i^5+ex_i^6+fx_i^7 - x_{i}^{2}y_i) = 0 \\ \frac{\partial S}{\partial d} &=& 2\sum_{i=1}^{N}(ax_i^3+bx_i^4+cx_i^5+dx_i^6+ex_i^7+fx_i^8 - x_{i}^{3}y_i) = 0 \\ \frac{\partial S}{\partial e} &=& 2\sum_{i=1}^{N}(ax_i^4+bx_i^5+cx_i^6+dx_i^7+ex_i^8+fx_i^9 - x_{i}^{4}y_i) = 0 \\ \frac{\partial S}{\partial f} &=& 2\sum_{i=1}^{N}(ax_i^5+bx_i^6+cx_i^7+dx_i^8+ex_i^9+fx_i^10 - x_{i}^{5}y_i) = 0 \end{eqnarray*}\]これらを変形すると、
\[\begin{eqnarray*} aN + b\sum_{i=1}^{N}x_i + c\sum_{i=1}^{N}x_i^2 + d\sum_{i=1}^{N}x_i^3 + e\sum_{i=1}^{N}x_i^4 &=& \sum_{i=1}^{N}y_i \\ a\sum_{i=1}^{N}x_i + b\sum_{i=1}^{N}x_i^2 + c\sum_{i=1}^{N}x_i^3 + d\sum_{i=1}^{N}x_i^4 + e\sum_{i=1}^{N}x_i^5 + f\sum_{i=1}^{N}x_i^6 &=& \sum_{i=1}^{N}x_{i}y_i \\ a\sum_{i=1}^{N}x_i^2 + b\sum_{i=1}^{N}x_i^3 + c\sum_{i=1}^{N}x_i^4 + d\sum_{i=1}^{N}x_i^5 + e\sum_{i=1}^{N}x_i^6 + f\sum_{i=1}^{N}x_i^7 &=& \sum_{i=1}^{N}x_{i}^{2}y_i \\ a\sum_{i=1}^{N}x_i^3 + b\sum_{i=1}^{N}x_i^4 + c\sum_{i=1}^{N}x_i^5 + d\sum_{i=1}^{N}x_i^6 + e\sum_{i=1}^{N}x_i^7 + f\sum_{i=1}^{N}x_i^8 &=& \sum_{i=1}^{N}x_{i}^{3}y_i \\ a\sum_{i=1}^{N}x_i^4 + b\sum_{i=1}^{N}x_i^5 + c\sum_{i=1}^{N}x_i^6 + d\sum_{i=1}^{N}x_i^7 + e\sum_{i=1}^{N}x_i^8 + f\sum_{i=1}^{N}x_i^9 &=& \sum_{i=1}^{N}x_{i}^{4}y_i \\ a\sum_{i=1}^{N}x_i^5 + b\sum_{i=1}^{N}x_i^6 + c\sum_{i=1}^{N}x_i^7 + d\sum_{i=1}^{N}x_i^8 + e\sum_{i=1}^{N}x_i^9 + f\sum_{i=1}^{N}x_i^10 &=& \sum_{i=1}^{N}x_{i}^{5}y_i \end{eqnarray*}\]となる。これらの連立方程式を解けばよい。
2. ガウスの消去法による連立1次方程式の解法について
当ブログ過去記事を参照。
- C++ - 連立方程式解法(ガウスの消去法)!
- Ruby - 連立方程式解法(ガウスの消去法)!
- Python - 連立方程式解法(ガウスの消去法)!
- Fortran - 連立方程式解法(ガウスの消去法)!
3. ソースコードの作成
- ファイル読み込み部分、計算部分、実行部分とソースファイルを分けている。
File: file.hpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
#ifndef REGRESSION_CURVE_5D_FILE_HPP_
#define REGRESSION_CURVE_5D_FILE_HPP_
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
class File {
std::string f_data;
public:
File(std::string f_data) : f_data(f_data) {}
bool get_text(std::vector<std::vector<double>>&);
};
#endif
File: file.cpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
#include "file.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
bool File::get_text(std::vector<std::vector<double>>& data) {
try {
// ファイル OPEN
std::ifstream ifs(f_data);
if (!ifs.is_open()) return false; // 読み込み失敗
// ファイル READ
std::string buf; // 1行分バッファ
while (getline(ifs, buf)) {
std::vector<double> rec; // 1行分ベクタ
std::istringstream iss(buf); // 文字列ストリーム
std::string field; // 1列分文字列
// 1行分文字列を1行分ベクタに追加
double x, y;
while (iss >> x >> y) {
rec.push_back(x);
rec.push_back(y);
}
// 1行分ベクタを data ベクタに追加
if (rec.size() != 0) data.push_back(rec);
}
} catch (...) {
std::cerr << "EXCEPTION!" << std::endl;
return false;
}
return true; // 読み込み成功
}
File: calc.hpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
#ifndef REGRESSION_CURVE_5D_CALC_HPP_
#define REGRESSION_CURVE_5D_CALC_HPP_
#include <cmath>
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
class Calc {
std::vector<std::vector<double>> data; // 元データ
std::vector<std::vector<double>> mtx; // 計算用行列
bool pivot(std::vector<std::vector<double>>&, unsigned int);
// ピボット選択
bool solve_ge(std::vector<std::vector<double>>&); // ガウスの消去法
public:
Calc(std::vector<std::vector<double>>& data) : data(data) {}
unsigned int cnt; // データ件数
bool reg_curve_5d(double&, double&, double&, double&, double&, double&);
// 単回帰曲線(5次)の計算
};
#endif
File: calc.cpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
#include "calc.hpp"
/*
* @brief 単回帰曲線(5次)の計算
*
* @param[ref] a (double)
* @param[ref] b (double)
* @param[ref] c (double)
* @param[ref] d (double)
* @param[ref] e (double)
* @param[ref] f (double)
* @return 真偽(bool)
* @retval true 成功
* @retval false 失敗
*/
bool Calc::reg_curve_5d(
double& a, double& b, double& c, double& d, double& e, double& f) {
unsigned int i; // loop インデックス
double s_x = 0.0; // sum(x)
double s_x2 = 0.0; // sum(xx)
double s_x3 = 0.0; // sum(x^3)
double s_x4 = 0.0; // sum(x^4)
double s_x5 = 0.0; // sum(x^5)
double s_x6 = 0.0; // sum(x^6)
double s_x7 = 0.0; // sum(x^7)
double s_x8 = 0.0; // sum(x^8)
double s_x9 = 0.0; // sum(x^9)
double s_x10 = 0.0; // sum(x^10)
double s_y = 0.0; // sum(y)
double s_xy = 0.0; // sum(xy)
double s_x2y = 0.0; // sum(xxy)
double s_x3y = 0.0; // sum(x^3y)
double s_x4y = 0.0; // sum(x^4y)
double s_x5y = 0.0; // sum(x^5y)
double x = 0.0; // x 計算用
double x2 = 0.0; // xx 計算用
double x3 = 0.0; // x^3 計算用
double x4 = 0.0; // x^4 計算用
double x5 = 0.0; // x^5 計算用
double x6 = 0.0; // x^6 計算用
double x7 = 0.0; // x^7 計算用
double x8 = 0.0; // x^8 計算用
double x9 = 0.0; // x^9 計算用
double x10 = 0.0; // x^10 計算用
double y = 0.0; // y 計算用
try {
cnt = data.size();
for (i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {
x = data[i][0];
y = data[i][1];
x2 = x * x;
x3 = x2 * x;
x4 = x3 * x;
x5 = x4 * x;
x6 = x5 * x;
x7 = x6 * x;
x8 = x7 * x;
x9 = x8 * x;
x10 = x9 * x;
s_x += x;
s_x2 += x2;
s_x3 += x3;
s_x4 += x4;
s_x5 += x5;
s_x6 += x6;
s_x7 += x7;
s_x8 += x8;
s_x9 += x9;
s_x10 += x10;
s_y += y;
s_xy += x * y;
s_x2y += x2 * y;
s_x3y += x3 * y;
s_x4y += x4 * y;
s_x5y += x5 * y;
}
// 行列1行目
mtx.push_back({(double)cnt, s_x, s_x2, s_x3, s_x4, s_x5, s_y});
// 行列2行目
mtx.push_back({s_x, s_x2, s_x3, s_x4, s_x5, s_x6, s_xy});
// 行列3行目
mtx.push_back({s_x2, s_x3, s_x4, s_x5, s_x6, s_x7, s_x2y});
// 行列4行目
mtx.push_back({s_x3, s_x4, s_x5, s_x6, s_x7, s_x8, s_x3y});
// 行列5行目
mtx.push_back({s_x4, s_x5, s_x6, s_x7, s_x8, s_x9, s_x4y});
// 行列6行目
mtx.push_back({s_x5, s_x6, s_x7, s_x8, s_x9, s_x10, s_x5y});
// 計算(ガウスの消去法)
if (!solve_ge(mtx)) {
std::cout << "[ERROR] Failed to solve by the Gauss-Ellimination method!"
<< std::endl;
return false;
}
// a, ..., f
a = mtx[0][6];
b = mtx[1][6];
c = mtx[2][6];
d = mtx[3][6];
e = mtx[4][6];
f = mtx[5][6];
} catch (...) {
return false; // 計算失敗
}
return true; // 計算成功
}
/*
* @brief ピボット選択
*
* @param[ref] 行列(配列) mtx (vector<vector<double>>)
* @param[in] 対象行
* @return true|false
*/
bool Calc::pivot(std::vector<std::vector<double>>& mtx, unsigned int k) {
unsigned int n; // 行数
unsigned int pv; // ピボット行
unsigned int i; // loop index
double v_max; // k 列絶対値の最大値
try {
n = mtx.size();
pv = k;
v_max = std::fabs(mtx[k][k]);
for (i = k + 1; i < n; ++i) {
if (std::fabs(mtx[i][k]) > v_max) {
pv = i;
v_max = std::fabs(mtx[i][k]);
}
}
if (k != pv) { swap(mtx[k], mtx[pv]); }
} catch (...) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
/**
* @brief ガウスの消去法(ピボット選択)
*
* @param[ref] 行列(配列) mtx (double)
* @return 真偽(bool)
* @retval true 成功
* @retval false 失敗
*/
bool Calc::solve_ge(std::vector<std::vector<double>>& mtx) {
int i; // loop インデックス
int j; // loop インデックス
int k; // loop インデックス
int n; // 元(行)の数
double d; // 計算用
try {
n = (int)mtx.size();
// 前進消去
for (k = 0; k < n - 1; k++) {
if (!pivot(mtx, k)) {
std::cout << "[ERROR] Failed to pivot!" << std::endl;
return false;
}
for (i = k + 1; i < n; i++) {
d = mtx[i][k] / mtx[k][k];
for (j = k + 1; j <= n; j++)
mtx[i][j] -= mtx[k][j] * d;
}
}
// 後退代入
for (i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
d = mtx[i][n];
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
d -= mtx[i][j] * mtx[j][n];
mtx[i][n] = d / mtx[i][i];
}
} catch (...) {
return false; // 計算失敗
}
return true; // 計算成功
}
File: regression_curve_5d.cpp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
/***********************************************************
単回帰曲線(5次回帰モデル)計算
: y = a + b * x + c * x^2 + d * x^3 + e * x^4 + f * x^5
: 連立方程式をガウス(ピボット選択)の消去法で解く方法
DATE AUTHOR VERSION
2022.06.20 mk-mode.com 1.00 新規作成
Copyright(C) 2022 mk-mode.com All Rights Reserved.
***********************************************************/
#include "calc.hpp"
#include "file.hpp"
#include <cstdlib> // for EXIT_XXXX
#include <iomanip> // for setprecision
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
std::string f_data; // データファイル名
std::vector<std::vector<double>> data; // データ配列
std::size_t i; // loop インデックス
double a; // 係数 a
double b; // 係数 b
double c; // 係数 c
double d; // 係数 d
double e; // 定数 e
double f; // 定数 f
try {
// コマンドライン引数のチェック
if (argc != 2) {
std::cerr << "[ERROR] Number of arguments is wrong!\n"
<< "[USAGE] ./regression_curve_5d <file_name>"
<< std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// ファイル名取得
f_data = argv[1];
// データ取得
File file(f_data);
if (!file.get_text(data)) {
std::cout << "[ERROR] Failed to read the file!" << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// データ一覧出力
std::cout << std::fixed << std::setprecision(4);
std::cout << "説明変数 X 目的変数 Y" << std::endl;
for (i = 0; i < data.size(); i++)
std::cout << std::setw(10) << std::right << data[i][0]
<< " "
<< std::setw(10) << std::right << data[i][1]
<< std::endl;
// 計算
Calc calc(data);
if (!calc.reg_curve_5d(a, b, c, d, e, f)) {
std::cout << "[ERROR] Failed to calculate!" << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// 結果出力
std::cout << std::fixed << std::setprecision(8);
std::cout << "---\n"
<< "a = " << std::setw(16) << std::right << a
<< "\n"
<< "b = " << std::setw(16) << std::right << b
<< "\n"
<< "c = " << std::setw(16) << std::right << c
<< "\n"
<< "d = " << std::setw(16) << std::right << d
<< "\n"
<< "e = " << std::setw(16) << std::right << e
<< "\n"
<< "f = " << std::setw(16) << std::right << f
<< std::endl;
} catch (...) {
std::cerr << "EXCEPTION!" << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
4. ソースコードのコンパイル
まず、以下のように Makefile を作成する。(行頭のインデントはタブ文字)
File: Makefile
gcc_options = -std=c++17 -Wall -O2 --pedantic-errors
regression_curve_5d: regression_curve_5d.o file.o calc.o
g++ $(gcc_options) -o $@ $^
regression_curve_5d.o : regression_curve_5d.cpp
g++ $(gcc_options) -c $<
file.o : file.cpp
g++ $(gcc_options) -c $<
calc.o : calc.cpp
g++ $(gcc_options) -c $<
run : regression_curve_5d
./regression_curve_5d
clean :
rm -f ./regression_curve_5d
rm -f ./*.o
.PHONY : run clean
そして、ビルド(コンパイル&リンク)。
$ make
5. 動作確認
まず、以下のような入力ファイルを用意する。
(各行は x と y の値)
File: data.txt
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
83 183
71 168
64 171
69 178
69 176
64 172
68 165
59 158
81 183
91 182
57 163
65 175
58 164
62 175
そして、ファイル名を引数に指定して実行。
$ ./regression_curve_5d data.txt
説明変数 X 目的変数 Y
83.0000 183.0000
71.0000 168.0000
64.0000 171.0000
69.0000 178.0000
69.0000 176.0000
64.0000 172.0000
68.0000 165.0000
59.0000 158.0000
81.0000 183.0000
91.0000 182.0000
57.0000 163.0000
65.0000 175.0000
58.0000 164.0000
62.0000 175.0000
---
a = 49991.44991036
b = -3652.20061146
c = 106.05865869
d = -1.52551761
e = 0.01087045
f = -0.00003070
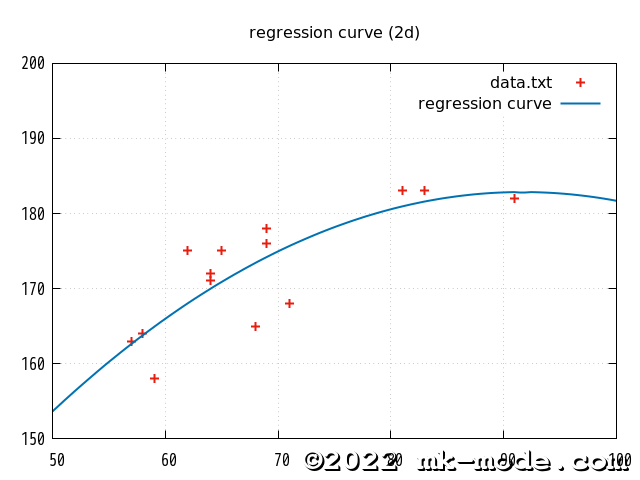
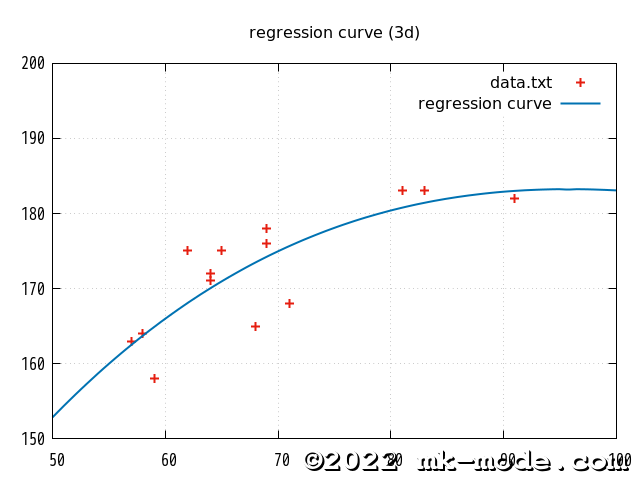
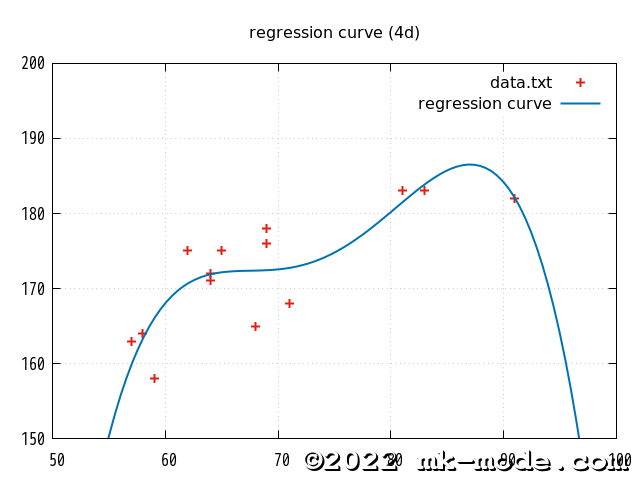
参考までに、上記で使用した2変量の各点と作成された単回帰直線を gnuplot で描画してみた。(比較用に2次、3次、4次も)
以上。

Comments